Extracting text from pdf`s is sometime more important than our dinner......
So here are 2 best ways
1) If not interested to download any software then go here....
http://www.pdftoword.com/Default.aspx
2) But if the files are protected then what ??
Here is the solution....A software called A-PDF text extractor, couple of screenshots are shown
below Now, what does that options include ??
Now, what does that options include ??
let me answer your question before you waste the internet bandwith by downloading it then then deleting it without any use...
So, where to download it from ??
here is the link
Download A-PDF Text Extractor
Comment below to thank me...



How to extract text from password protected pdf file ?
1 comments Filed Under:
How to install Red had Linux ?
This is an exclusive article regarding installation if Linux.
The reason for this post is that I dont want my friends to face similar problems as I did during my Installation....... :(
So to start with, First see which Linux are you installing ? Its totally a matter of choice.... If you are with anything other than Red Hat 9 Setup then most probably you wont have any problem as far as Detection of Hard disk.
But for RH9 its a compulsion that your HDD must be primary master [:P], Here comes the difficulty.
Most of us dont know all there this, so for those who don't know please google it what is Primary Master Primary Slave,Secondary Master and Secondary Slave.
Now if you have an IDE drive (HDD) this is not an issue but for those with SATA (like me) a big issue arises at the start itself, So how to solve this probelm ?
Here is the solution....
Now again this solution vary with the Mainboard you are using but the fundamentals will remain same.
For mine board (MSI) it was like
go to your BIOS, then In integrated device configuration for SATA devides mostly it is in Enhaced mode which supports 2 IDE and 4 SATA (may vary depending upon the board cost)
Here you have to change the mode to Disable. And connect you HDD to the SATA0 pin on your board.
Done.
Now your HDD is primary master.
so some boards like Intel :
Steps to be followed are as follows :
1. Go to BIOS Setup utility by pressing DEL Key.
2. In BIOS you have menus which are listed below
|Main
|Advanced--->|Drive Configuration
|Security |
|Power |
|Boot |
|Exit |
3. In Advanced Menu select "Drive-IDE-Configuration"
4. "Drive-IDE-Configuration" has following
Default options :
..........
..........
ATA/IDE Configuration [Enhanced] ---> Press Enter / Select [Legacy]
If Legacy is selected then below ATA/IDE Configuration an option
called Legacy IDE Channels is shown where :
5. By Default it will detect other option , but if you have SATA
Hard Disk connected to your Primary SATA and CD or CDRW to your
Secondary Master then you have to select [SATA P0/P2, PATA] by
pressing enter. You will get other options also which are :
[SATA P0/P2, P1/P3]
[SATA P1/P3, PATA]
[SATA P0/P2, PATA] --> Select this option
[PATA only]
6. Try other options according to your drives connected.
In this post I concentrated on just how to make your HDD the primary master for particularly RH9 which is most used for Servers all over the world.
Soon I will post how to make you partitions and the significance regarding them....
0 comments Filed Under: how, install, linux, red hat
How is the structure of a hard disk ?
On this page, I’ll cover file structure on a hard drive. Tracks, sectors, cylinders, etc. Plus I’ll cover what happens when you format and partition a drive.
Basically, tracks, sectors, and cylinders are the divisions of the hard drive platters where information is stored. A track is a concentric ring around the platter containing information. Since a hard drive typically has two or more platters, each storing data on both sides, these tracks line up on each platter. The identically positioned tracks on each platter are called cylinders. To better help you understand a track and cylinder, let’s take a target used for target practice. You have a bunch of concentric circles, each bigger than the other, all sharing the same center, which is the bulleye. Now, each of the spaces between circles is similar to a track on a hard disk platter. Now, if you stack several of these targets on top of each other, each exactly the same, you can form a cylinder by simply taking a track and moving it down through all of the same tracks on the targets below.

Since typical hard drives are too large to deal with by the track, each track is divided into sectors. Its not that a track could not be dealt with, but since a track can hold as much as 50K sometimes, this would not be practical for storing large files. So, sectors are basically slices of the track. Different drives have different numbers of sectors per track.
Each sector is given an identity during low-level formatting to aid the controller in finding what it needs in the appropriate sector. These sector numbers are written to the beginning and the end of each sector, called the prefix portion and the suffix portion respectively. These identities take actual space on the hard drive. This explains why there is a difference between the capacity of an unformatted disk and a formatted one. On a floppy, the disk itself can hold 2M or so of data. When formatted and the identities placed, the capacity reduces to 1.44M. The same holds true for a hard drive. Drive manufacturers know this and publish formatted capacities to indicate drive size.
There are two types of disk formatting: low-level and high-level. These both are done in the preparation of a hard drive for use. First, one low-level formats, then partitions, then high-level formats. A low-level format turns the platter from a blank slate to a divided slate. It defines the data areas: creates tracks, separates into sectors, and writes the ID numbers to each sector. Low-level formatting typically has to be done using a specific utility released by the manufacturer of the drive. Almost all drives sold are already low-level formatted at the time of sale. In most cases, you do not need to ever do it again.
Partitioning segments the drive into separate areas, each capable of running its own operating system. At this point, the hard drive needs to be high-level formatted. High level formatting is the type of formatting most people think of when thinking of formatting. During high-level formatting, the file allocation tables (FATs) are dropped in. This is a “table of contents” for the drive, allowing the drive to later find files on the drive whereever they sit on the platter. The drive cannot be used until it is high-level formatted. This can be performed with the DOS FORMAT command, through Windows (if the drive is not master), or through a third party utility.
There are four types of file systems.
- FAT16. The is the file system used by DOS, Win95 and Win98, unless you convert. It supports an eight letter file name max, with a three letter extension under DOS. With Windows it supports up to 255 characters. With this system, a partition can be no larger than 2G.
- FAT32. The 32 means 32-bit. This is an optional file system introduced with Windows 95 OSR-2. The file allocation units are stored as 32-bit numbers. The main advantage is that it allows for partitions of up to 2048G with smaller clusters. There is an option to convert FAT16 to FAT32 under Windows 98, and Windows NT5 will support it as an option.
- High Performance File System (HPFS). An unpopular file system only used with OS/2 or early versions of NT. File names can be 256 characters and partitions can be 8G.
- Windows NT File System (NTFS). Just like the HPFS, but only for NT.
The FAT file system (specifically FAT32) is most used in PC’s today. The main problem with the original FAT16 was the inefficient use of disk space when defining clusters, or groups of sectors. The clusters were rather large, causing wasted space because a small file would still take up the entire cluster even though that cluster could hold more. With FAT32, 4 billion clusters are allowed, ultimately allowing 4K clusters. This significantly reduces disk waste. The concept of FAT explains why one can run out of disk space even when you are not storing the disk’s full capacity in files. For example, a 1G hard drive can run out of space with 160MB to spare. This is due simply to the FAT structure. With the original FAT, each cluster could hold 32K. But, if you are storing an 8K file, it still takes up a complete cluster, leaving the other 24K to waste. This wasted space is called slack. The only way around this is to re-partition the hard drive to two or more partitions. As the partition gets smaller the wasted space gets less. This, then is a tradeoff. The convenience of one partition, or the wasted disk space. With FAT32, the wasted space is much less because of the smaller clusters.
No matter what file system is used, a boot sector is written to the beginning of each disk in the first sector. This sector contains the boot program which tells the system what to do when you first turn it on. This is called the boot sector.
That completes the basic view of how files are stored on a hard drive.
0 comments Filed Under: hard disk, how, ntfs
Tata docomo gprs settings for 2010
If you have any problems for GPRS settings for your TATA docomo gprs setting and need guide for proper settings for proxy or port number then the following setting can be very help ful for you..
Connection Name : any name
Data Bearer: GPRS
Access Point Name :anyname(same as above)
Username: Blank
Password: Blank
Homepage: http://wap.google.com
Connection :Security Off
Session Mode: Permanent
If you have WAP 2.0 compliant phones there need to be some more settings to be changed
Go to >>Under Options Advanced Settings and then::
Phone IP Address: Automatic
DNS Address :Automatic
Primary name server: 0.0.0.0
Second name server :0.0.0.0
Proxy server address: None
Proxy port number :0
If i have not mentioned the edits that you still get in your mobile then it means you need to leave them as default as it is..
1 comments Filed Under: gprs, tata docomo
IPL updates for free..
Latest 2010 tricks and hacks to get free Cricket updates including IPL 2010 for free in your mobile there follow the following instructions..
type CRI and send it to 9773300000.
After that again type ON and send it to 9773300000.
100% working! worked for me hope it works for you too..
it s a latest 2010 tricks and service provided by google
0 comments Filed Under: ipl
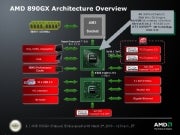
AMD's 890GX Chipset Offers HD For Less
AMD has announced its new 890GX chipset, the latest generation of its integrated graphics platform, and the first chipset to natively support SATA 6 Gb/s.
While Intel's Arrandale and Clarkdale integrated graphics bundle a GPU onto the CPU, AMD's solution is built right into the motherboard, and offers a relatively inexpensive platform with impressive potential for scalability.

For our tests, AMD provided the new Gigabyte 890GPA-UD3H, one of the first motherboards to support the new 890GX chipset. For comparison, we used a Gigabyte motherboard equipped with the 785G chipset. Introduced last August, the 785G chipset offers an integrated ATI Radeon HD 4200 graphics processor, versus the 890GX's Radeon HD 4290. Both graphics chips support DirectX 10.1, and the chief difference between them is their core clock: the Radeon HD 4200 runs at 500MHz, while the 890GX's Radeon HD 4290 runs at 700MHz.
We also used a pair of the recently launched 2.9 GHz AMD Athlon II X4 635 CPUs. Beyond the motherboards, our testbeds were identical: 4GB of RAM, 1TB hard drives, and optical drives for loading software.
The 890GX showed negligible improvement over the 785G chipset in our WorldBench 6 test suite, scoring a 110 over the 785G's 109. The 890GX began to pull away from the 785G during our graphics tests, but overall gaming performance is poor -- as expected, for an integrated graphics chip.
Running at 1024 x 768 resolution on medium settings, Unreal Tournament 3 saw an almost-playable 28.4 frames per second, versus the 785G's 21.4 frames per second. World in Conflict fared worse: at a resolution of 1366 x 768, medium settings, we saw 15 frames per second on the 890GX, and a paltry 10 frames per second on the 795GX.
Enthusiast level gaming wasn't much of an option, but high-definition media playback was promising. Playback was crisp and smooth, and CPU utilization wavered between a negligeble 10% and 13% while watching high-definition clips on both chipsets. The Radeon HD 4290 and HD 4200 both sport the Unified Video Decoder 2.0 technology, which supports MPEG-2 and H.264 decoding, as well as multi-monitor support, and Blu-ray playback with support for picture-in-picture functionality.
To our surprise, power consumption took a slight dip with the 890GX.Our meters hovered at 69.1 watts while our test system was idle, as opposed to the 785G's 77.5 watts. Under peak performance that difference evaporated -- 101.1 for the 890GX, and 100.2 for the 785G.
The integrated graphics may steal the limelight, but the 890GX chipset's defining characteristic is its updated southbridge -- dubbed the SB850. A Northbridge - Southbridge architecture is a standard feature of chipsets on a PC. The northbridge is responsible for interfacing with high-speed components, like the processor and memory. The southbridge controls lower-speed PC peripherals, such as hard drives, or USB ports.
The SB850 southbridge provides the aforementioned SATA 6 Gb/s support, a definite boon for digital packrats who enjoy speedy transfer rates of about 500MB/s. That bandwidth is made possible by AMD's 2 GB/s Alink Express III interface, which alleviates performance bottlenecks between the northbridge and the southbridge. And as AMD has so kindly pointed out, Intel's latest H55 and H57 chipsets deliver about half that bandwidth.
While final configurations will vary by motherboard model, the 890GX chipset offers a wide swath of connectivity options. It can support up to six SATA 6 Gb/s ports, 14 USB 2.0 ports, and two PCI Express 2.0 x16 slots -- these will run as x8 slots, should you have a pair of GPUs installed. There's no native USB 3.0 support however: our Gigabyte board offers USB 3.0 through an NEC host controller, and it'll be up to individual motherboard manufacturers to implement on their own.
Motherboard prices will also vary, but ASUS, MSI, and Gigabyte have released pricing estimates wavering between $130 and $180. Whether or not the chipset is worth the cost will depend upon an individual's needs. If you purchased a motherboard sporting the 785G chipset when it was announced, or have no interest in the performance benefits of SATA 6 Gb/s, you aren't likely to notice a difference in performance.
But the 890GX's greatest potential lies in its scalability. Motherboard-based integrated graphics allow system builders on a tight budget to piece together an inexpensive system, that's still suitable for high-definition media playback. As SATA 3.0 sees widespread adoption and prices fall, the 890GX's full 6Gb/s transfer rates will be the fastest game in town. And with a pair of PCI Express 2.0 graphics slots, you'll be able to add discrete graphics cards, expanding into Crossfire territory at your leisure. As an AM3 socket system, it'll support current CPUs, and compatibility is planned for AMD's upcoming Phenom II X6 processors, previously codenamed "Thuban."
If you're not interested in gaming, AMD's Dual Graphics technology will likely pique your interest. It combines their integrated graphics chips with their more inexpensive discrete cards, offering considerable performance gains, at bargain basement prices. While the preview is currently limited to the ATI Radeon 4200 and the $60 Radeon HD 5450 discrete graphics card, it will be of special interest to users looking for an inexpensive way to boost their performance.
All things considered, AMD's 890GX is readily expandable, sports tomorrow's tech, and is relatively cheap -- if you're in the market for a new PC, and want HD on the cheap, check back for more news on the 800-series.
0 comments Filed Under:
Latest mobile trick in India
JUST FOLLOW THESE SIMPLE STEPS
1- GO TO "http://www.your-freedom.net"
AND CREATE UR FREE ACCOUNT AND ALSO CONFIG UR FREEDOM MAIL
2=DOWNLOAD FREEDOM -
Download Your freedom From HERE
12MB
3-INSTALL IT AND GO TO
Start Your Freedom.under "configure>account information" enter you username and password correctly.(which we created in step1)
4-In the server connection tab select connection mode as udp.
Enter address 208.53.158.27 port 53 Don’t click on wizard just save & exit
5-YF MAIN MENU>PORTS>CLICK ON ALL OPTIONS
7-THEN CHANGE ACCES POINT NAME(APN)
IN PC SUIT OR BLUETOOTH,
Airtel-airtelgprs.com
idea-internet n more according to ur network for pc use
[IF U KNOW THESE STEP SKIP IT] -GO TO MENU CLICK ON CONTROL PANEL>PHONE N MODEM >MODEMS>SELECT UR MODEM U R USING>PROPERTIE>ADVANCE>CHANGE APN AS UR NETWORK
NOW LOUNCH UR FIRE FOX ENJOY FREE DOWNLOADING N SURFING NET
U CAN USE IT ONLY 6 HOURS IN ONE DAY
AND 18HOURS IN WEEK, AND GOOD THING IS THAT U CAN USE IT FREE IN ANY NETWORK, I M USING IT,
ENJOY
IT WORK ON ALL NETWORKS ALSO WORKS IN NEGATIVE BALANCE
PLEASE LEAVE YOUR COMMENTS...
0 comments Filed Under:
Difference between Intel Core 2 Extreme / Quad / Duo vs Core i7 / i5 processors
Since its launch in late 2008, the Nehalem based Intel Core i7 processors are getting low on price and becoming mainstream processors. As a buyer, when you are searching for a PC or notebook, with Core2 range of products, now you may see Core i7 based systems are up for sale at a very competitive price.
They look very similar from their specifications, like both processors are Quad Core, operates at a similar frequency and shares almost same features like, both supports Intel VT, Intel 64, Execute Disable Bit, Speedstep Technology, Enhanced Halt State, 45mn technology and so on.
So what should you buy and why should you buy ?
Conroe (Core2) vs Nehalem (Core i7)
Core2 and Core i7 comes with a completely different processor architecture. All the available Core2 processors (Conroe, Allendale, Wolfdale) have evolved from the original Intel Core architecture Conroe where as Core i7 processors are based on a completely new architecture called Nehalem.
Processing speed and performance depends on couple of things. First the speed or rather the operating frequency second but most important the way by which it is processes a matter.
We already have seen, Intel Dual Core processor E2140 operating 1.6 GHz can out perform a Intel Pentium D 820 processors operating at 3.0 GHz while consuming less power, just because the Core architecture is much better than the age old Pentium brand.
Similar way, the Nehalem architecture is much faster and power efficient than older Core2 range.
Native Quad Core
Intel Core i7 processors have 4 native cores meaning there are 4 different cores given on a single physical die compare to Core 2 Quad where we have 2 die having 2 cores each merged together.


It allows the Core i7 processors to utilize the processor cache more efficiently than Core 2 Quad processors.
L3 Cache
Compare to Intel Core2 which comes with large L2 cache, Intel Core i7 processors include a large amount of L3 cache along with L2 also.
Core i7 processors having 256 KB of L2 for each core (256KBx4) where as a large 8 MB of L3 available as shared among all the 4 cores, is much faster thanCore 2 Quad where we have a large L2 cache is been shared between 2 dies and 2×2 cores.
Hyper-Threading is back
Yeah.. That age old feature which we have first seen in case of Intel Pentium EE processors is back with Intel Core i7. Each and every core of Intel Core i7 processors can process 2 threads simultaneously, thus appearing as a 8 core processor to the Operating system.
All though the feature didn’t click with Pentium architecture but with Nehalem it seems to help a lot with todays new multi-core based applications.
Goodbye FSB and welcome QPI
QPI is something, which is not new in market, as AMD is using it for quite some time but its something new for Intel, as finally they are saying goodbye to the traditional method of connecting various part of the CPU.


We already have seen the benefit of QPI (Quick Path Interconnect) with AMD’s Hypertransport. However, Intel’s QPI under Nehalem seems to have beaten AMD in their own game as Core i7 with QPI is much faster than AMD HyperTransport 3.0.
Adopting QPI gives Intel another great option to access memory directly via their Memory on Die Controller. As you may see, under QPI, Core i7 processor can now directly access memory as they are equipped with a memory control given directly on the processor die.
The x58 and Socket 1366
Finally after so many years, Intel replaced the socket LGA775. Intel Core i7 processor comes under a new larger socket named LGA 1366 and LGA 1156 (core i5).
Intel Core 2 platform has option to chose from many available Intel or Nvidia or ATi chipsets where as till now, Core i7 supports only one chipset, the Intel x58 but x58 seems to out perform any and every available option of Core2 platform.

Earlier one had to chose between either ATi or Nivida as platform before selecting motherboard as with Core2 you can either run SLi or CrossFire. But with x58 that problem is solved. You can run any of these multi-GPU setup from x58 or rather single motherboard.
(But that doesn’t mean you can bridge 2 different company simultaneity)
Compare to Core2 which can support both DDR-III and DDR-II, Core i7 in combination with x58 is just DDR-III only. It may sound a downer, but as DDR3 is becoming mainstream, your PC should have the fastest option.
Few new features
Intel Demand Based Switching (DBS)
Its a new form of older version, that’s Intel SpeedStep. What it does is, it lowers the processor frequency and power consumption under idle state when system doesn’t require heavy processing. The processor returns to full power only when OS requires. It saves a lot of energy and noise also as lowerfrequency means less heat hence even the processor FAN can run at lower RPM generating less noise.
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
Performance on demand, as what Intel calls it. It allows Core i7 CPUs to actually overclock it self to run higher than its originalfrequency . Just opposite of what (DBS) does. Turbo boost works in tandem with Intel VT / Intel HT. Turbo boost actually can overclock individual cores, when they are in need of extra juice under certainly muti-core applications like heavy duty CAD / CAM or editing or virtualizing.
Along with these new features and upgrades to existing technology, Intel Core i7 or Core i5 processors make them self an excellent purchase over their predecessor. Therefore, if you are looking for a new computer with Intel based setup, try and see if you can get your self a Core i7 or Core i5 based system.
Intel Core i7 processors are available from USD 280 to $1000 where as there are hundreds of choice for motherboards under LGA 1366 and LGA 1156
0 comments Filed Under: processors
Intel core 2 duo vs Intel dual core vs Intel Pentium D
Many people are confused what exactly the difference between Intel Core 2 Duo and Between Intel Pentium D or Intel Dual Core processors….
I would try to explain from a END user point a view rather not going in to details architecture over view…
The Simple facts are,
All Core 2 Duo Processors are Dual Core Processors..
All Pentium D Processors are Dual Core Processors..
All Intel Dual Core Processors are Dual Core Processors…



Pentium D is nothing but 2 Prescott Processors side by side… runs very hot, not a good OverClocker…
Intel Core 2 Duo processors are next gen processors from Intel on 65 nm platform… developed from Ground up with new Architecture called Core… so they are whole new Processors just Jump like Pentium 2 to Pentium 3 or Pentium 4… Expect one Core 2 Duo Lowest End Processors like E4400/E4300 taking up and beatingIntel Pentium D 3.8 GHz ones with ease ![]() … runs damn cool and super over clocker…
… runs damn cool and super over clocker…
Intel Dual Core Processors are just launched striped down version of Core 2 Duos.. there are 2 in Market for Desktop range, E2140 runs at 1.6 GHz with 1 MB L2 and 800 MHz FSB and E2160 with 1.8 GHz with same specs of E2140…. these are not Pentium D rather they are same batch like Core 2 Duo based on the new Core Technology…. they perform same like Core 2 Duos but they were launched with a very low price to counter the market of super low cost but high performer AMD X2 range line up to AMD X2 4000….
0 comments Filed Under: core2duo, intel, processor
Google Search Engine Hidden Features
In addition to providing easy access to billions of web pages, Google has many special features to help you to find exactly what you’re looking for. Click the title of a specific feature to learn more about it.
| • Book Search | Use Google to search the full text of books. | |
| • Cached Links | View a snapshot of each page as it looked when we indexed it. | |
| • Calculator | Use Google to evaluate mathematical expressions. | |
| • Currency Conversion | Easily perform any currency conversion. | |
| • Definitions | Use Google to get glossary definitions gathered from various online sources. | |
| • File Types | Search for non-HTML file formats including PDF documents and others. | |
| • Groups | See relevant postings from Google Groups in your regular web search results. | |
| • I’m Feeling Lucky | Bypass our results and go to the first web page returned for your query. | |
| • Images | See relevant images in your regular web search results. | |
| • Local Search | Search for local businesses and services in the U.S., the U.K., and Canada. | |
| • Movies | Use Google to find reviews and showtimes for movies playing near you. | |
| • Music Search | Use Google to get quick access to a wide range of music information. | |
| • News Headlines | Enhances your search results with the latest related news stories. | |
| • PhoneBook | Look up U.S. street address and phone number information. | |
| • Product Search | To find a product for sale online, use Google Product Search. | |
| • Q&A | Use Google to get quick answers to straightforward questions. | |
| • Refine Your Search – | Add instant info and topic-specific links to your search in order to focus and improve your results. | |
| • Results Prefetching | Makes searching in Firefox faster. | |
| • Search By Number | Use Google to access package tracking information, US patents, and a variety of online databases. | |
| • Similar Pages | Display pages that are related to a particular result. | |
| • Site Search | Restrict your search to a specific site. | |
| • Spell Checker | Offers alternative spelling for queries. | |
| • Stock and FundQuotes | Use Google to get uptodate stock and mutual fund quotes and information. | |
| • Street Maps | Use Google to find U.S. street maps. | |
| • Travel Information | Check the status of an airline flight in the U.S. or view airport delays and weather conditions. | |
| • Weather | Check the current weather conditions and forecast for any location in the U.S. | |
| • Web Page Translation | Provides you access to web pages in other languages. | |
| • Who Links To You? | Find pages that point to a specific URL. |
0 comments Filed Under: features, google, hidden, search words